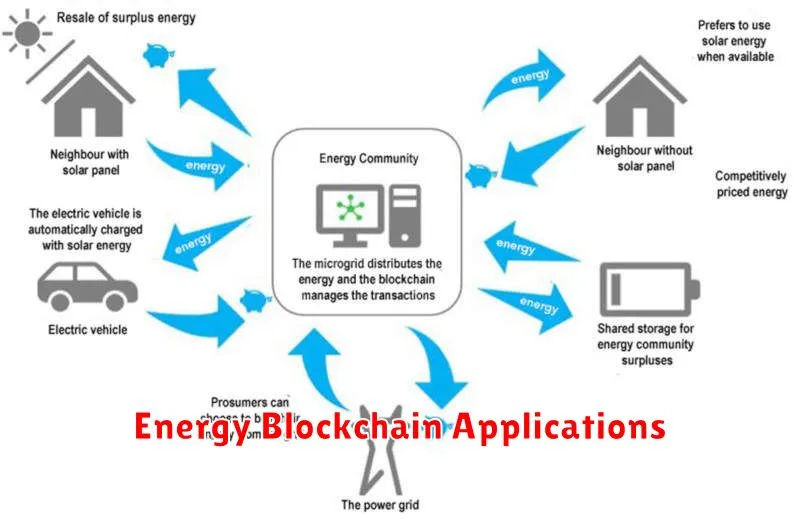
The energy sector is ripe for disruption, and blockchain technology is emerging as a key player in driving this transformation. This article explores five groundbreaking blockchain applications poised to revolutionize the energy industry, impacting everything from renewable energy trading and grid modernization to improved energy efficiency and enhanced security. Discover how blockchain’s decentralized and transparent nature can unlock new levels of efficiency, security, and sustainability within the complex landscape of energy production, distribution, and consumption.
Decentralized Energy Trading
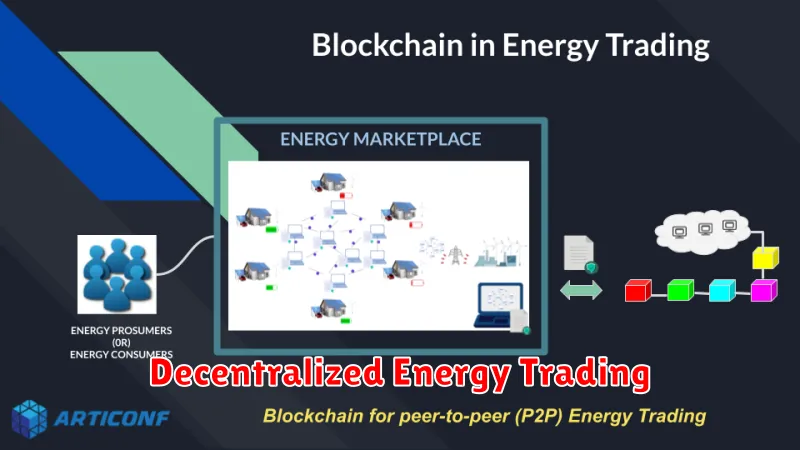
Decentralized energy trading leverages blockchain technology to facilitate peer-to-peer (P2P) energy transactions, bypassing traditional intermediaries like utility companies. This creates a more efficient and transparent energy market.
Smart contracts automate the agreement and transfer of energy, ensuring secure and verifiable transactions. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, are particularly well-suited for this model, allowing producers to directly sell excess energy to consumers within a local microgrid or broader network.
The benefits include reduced transaction costs, increased energy independence, and greater integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. The transparency and immutability of blockchain enhances trust and accountability among participants.
Challenges remain, including scalability, regulatory hurdles, and the need for robust cybersecurity measures. However, decentralized energy trading holds significant potential for transforming the energy sector and empowering consumers and producers alike.
Blockchain for Carbon Credit Management

The energy sector is a significant contributor to global carbon emissions. Blockchain technology offers a promising solution for improving the management of carbon credits, which represent verified reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
A key challenge in the current carbon credit system is a lack of transparency and efficiency. Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable ledger can create a more transparent and auditable system. This enhanced transparency reduces the risk of fraud and double-counting, ensuring the integrity of carbon credits.
By recording carbon credit transactions on a blockchain, all participants—from project developers to buyers—have access to a shared, verifiable record. This increased traceability simplifies the verification process, accelerates transactions, and reduces administrative costs. Furthermore, smart contracts can automate the process of issuing, transferring, and retiring carbon credits, streamlining operations and increasing efficiency.
The use of blockchain in carbon credit management ultimately enhances trust, improves accountability, and fosters greater participation in carbon offsetting programs, facilitating the transition to a lower-carbon economy.
Enhancing Grid Security with Blockchain
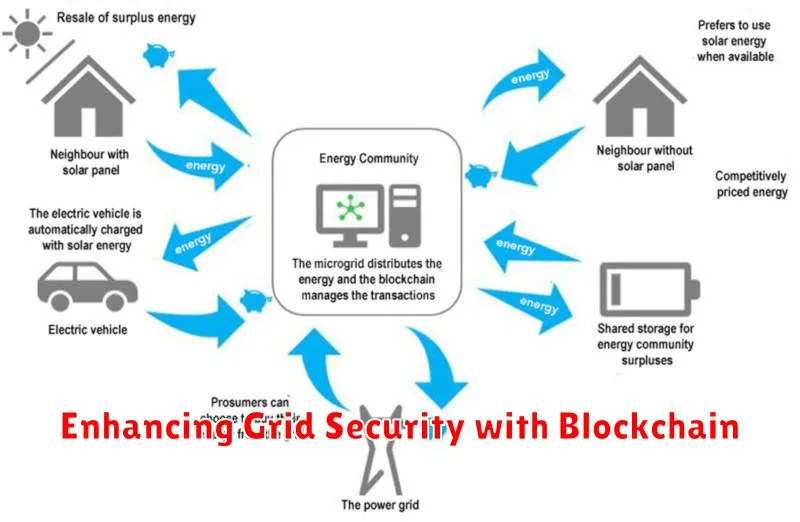
Blockchain technology offers a promising solution to enhance the security of energy grids. Its decentralized and transparent nature makes it resistant to single points of failure and manipulation.
By recording energy transactions and grid operations on a shared, immutable ledger, blockchain can improve data integrity and authenticity. This prevents unauthorized access and manipulation of critical grid data, thereby mitigating risks associated with cyberattacks and fraud.
Furthermore, the use of smart contracts on the blockchain enables automated and secure transactions, streamlining processes and reducing the potential for human error. This increased automation can lead to improved grid management and efficiency.
Blockchain’s ability to facilitate secure microgrids and peer-to-peer energy trading further enhances resilience and flexibility within the energy grid. This distributed approach reduces reliance on centralized control points, strengthening the overall grid’s security posture.
In summary, the application of blockchain technology can significantly strengthen the security of energy grids, offering enhanced data integrity, improved automation, and increased resilience against threats.
Tracking Renewable Energy Certificates
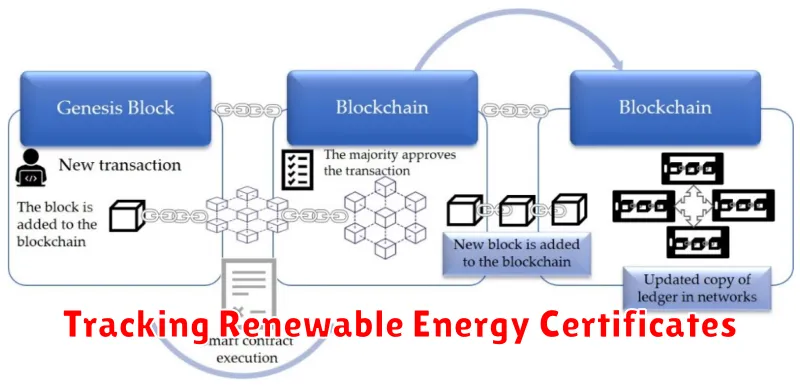
Blockchain technology offers a transparent and secure solution for tracking Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs). RECs, also known as Green Tags, represent proof that one megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity was generated from a renewable source. Currently, REC tracking often suffers from inefficiencies and lack of transparency, leading to potential fraud and double-counting.
A blockchain-based system can record each REC’s origin, transfer history, and retirement status on a decentralized, immutable ledger. This enhances transparency and verifiability, ensuring that RECs are not traded or retired multiple times. This increased trust reduces the risk of fraudulent activities and builds confidence in the renewable energy market.
Furthermore, blockchain can streamline the entire REC trading process, reducing administrative overhead and transaction costs. Automation of transactions through smart contracts can significantly improve efficiency and speed up the process of verifying and transferring RECs.
The improved security and traceability offered by blockchain facilitates accurate reporting and compliance with renewable energy mandates, providing greater accountability for both producers and consumers of renewable energy.
Optimizing Energy Distribution

Blockchain technology offers a promising solution for optimizing energy distribution by enhancing grid management and peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading. Smart contracts automate energy transactions, improving efficiency and transparency.
Real-time tracking of energy flow and consumption data, facilitated by blockchain’s immutable ledger, allows for more accurate demand forecasting and efficient resource allocation. This reduces waste and improves grid stability.
Blockchain also enables the development of microgrids and decentralized energy systems. These systems are more resilient to outages and can better integrate renewable energy sources. The secure and transparent nature of blockchain facilitates efficient energy sharing amongst participants within the microgrid.
Furthermore, improved billing and payment systems, driven by smart contracts, streamline the process for both consumers and energy providers. This improves accuracy and reduces disputes, leading to greater trust and transparency within the energy sector.